The Powers of Two: Why Is 1 + 2 + 4 + 8 + … = -1
On calculating infinite divergent series sums

The Short Answer
To satisfy you’re curiosity and save you from the mathematical jargon, the simple explanation is just:
x = 1 + 2 + 4 + 8 + …
x = 1+ (2 + 4 + 8 + …)
x = 1+ 2(1 + 2+ 4 + 8…)
x = 1+ 2x
x = -1
This
is almost the exact same method you would use for a convergent infinite
series, by taking advantage of the common ratio of the sequence and the
nature of infinity. But while convergent series, like 1/2 + 1/4 + 1/8 +
1/16…, can easily be visualized and comprehended, divergent series are
much more incoherent.
Nonetheless,
if you would join me in the scenic route, perhaps we can stumble upon a
few more answers and — even better — more insightful questions.
Divergence vs Convergence
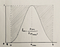
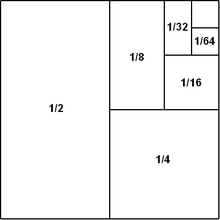
A convergent series is one whose sum approaches a limit.
For
instance, the convergent series 1/2 + 1/4 + 1/8 + 1/16 + … clearly
approaches a certain limit, which is 1, as made apparent by the
geometric illustration below.
Partial Sums
We
can also differentiate divergence and convergence by their partial
sums. As the name suggests, a partial sum is a sum of a part of a
series. We can express the partial sum of the first n terms of 1/2 + 1/4
+ 1/8 … using the formula for a geometric series.

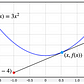
Applying
that formula, we see that the partial sums of a convergent series seem
to approach one, which is made even more evident by graphing it.

In the case of divergence, however, the partial sums do not approach a value but extends to infinity

‘Rules’ For Calculating Infinite Divergent Series
Although
doing so is comparatively less straightforward, it is still possible to
get the sum of a divergent series — as long as we follow a few rules.
Regularity
A summation method is regular if the sum it gives for a convergent series is the limit of its partial sums

Linearity
To be linear, sums must be distributable and factorable


In a linearity, terms of a summation of equal length can be grouped.

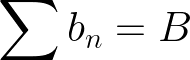

Stability
Stability is present when terms can be “extracted” from a summation


Applications to power of two
x = 1 + 2 + 4 + 8 + …
(1) x = 1+ (2 + 4 + 8 + …)
(2) x = 1+ 2(1 + 2+ 4 + 8…)
x = 1+ 2x
x = -1
Taking
the long route has its benefits. If you paid attention, you would
notice that our initial solution is not completely regular. This is
because the limit of the divergent series is infinity, and yet we gave a
finite value as an answer. Yet we can show that it does comply with
linearity and stability.
(1) x = 1+ (2 + 4 + 8 + …)
In (1), we were able to extract a term from the summation, this is equivalent to

Hence we can say that the summation method is stable.
(2) x = 1+ 2(1 + 2+ 4 + 8…)
With (2), we were able to factor out 2 from a summation, which is the same as

And finally, this shows that the series is linear.
The Long Answer
So given this, we can say that 1 + 2 + 4 + 8 + … is not completely
-1, because the summation method we used — although linear and stable —
is not totally regular. Totally regular summations would say infinity
is an answer.
What’s the real answer? Depends which requirement you prioritize.
But
it’s not always about finding the answer, is it? Just grappling with
infinite divergent series can lead us to some interesting insights, and
even — as Leonhard Euler has shown us — to profound discoveries on
mathematics as a whole.
All it takes is time and patience.
Source
Sums Of Divergent Series. Brilliant.org. Retrieved July 1, 2020, from https://brilliant.org/wiki/sums-of-divergent-series/
Living the complexity of the unknown and the uncertainty of the everyday | www.joaquindecastro.gq
Medium’s #1 Math Publication!
More From Medium
Welcome to a place where words matter. On Medium, smart voices and original ideas take center stage - with no ads in sight. Watch
Follow all the topics you care about, and we’ll deliver the best stories for you to your homepage and inbox. Explore
Get unlimited access to the best stories on Medium — and support writers while you’re at it. Just $5/month. Upgrade