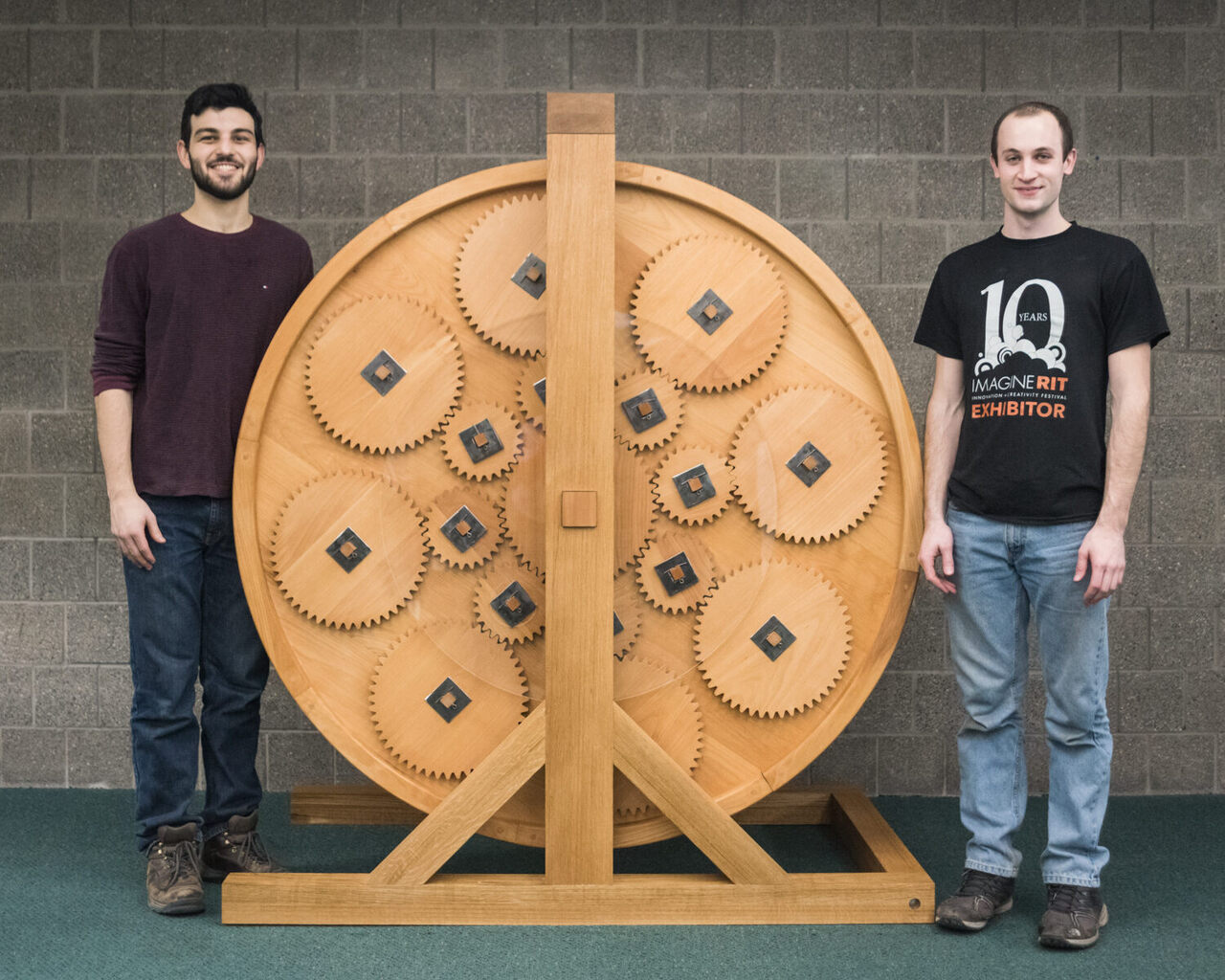
How Students Built a 16th-Century Engineer’s Book-Reading Machine
The bookwheel helps readers browse eight texts at once. The only problem? It weighs 600 pounds.
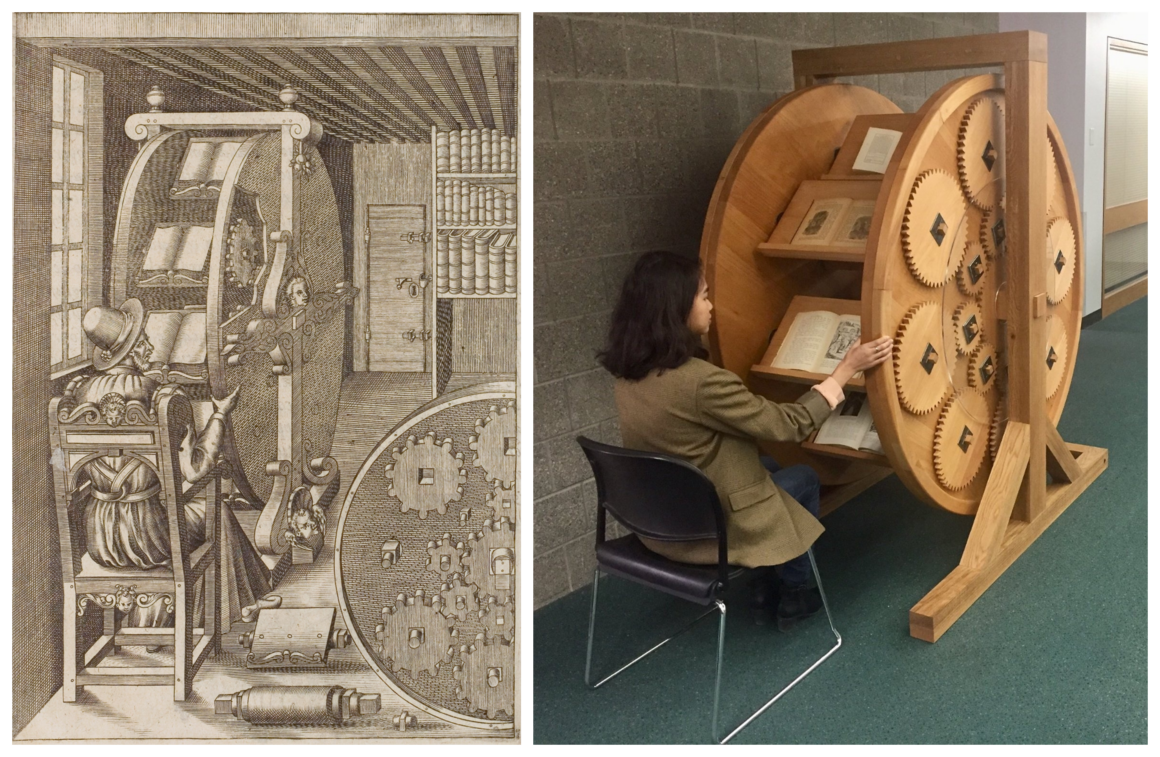
Agostino Ramelli, the 16th-century Italian military
engineer, designed many contraptions for the changing Renaissance
landscape, including cranes, grain mills, and water pumps. But his most
compelling apparatus was one meant to nurture the mind: a revolving
wooden wheel with angled shelves, which allowed users to read multiple
books at one time. “This is a beautiful and ingenious machine, very
useful and convenient for anyone who takes pleasure in study, especially
those who are indisposed and tormented by gout,” Ramelli wrote in Le diverse et artificiose machine, his illustrated magnum opus of mechanical solutions. “Moveover, it has another fine convenience in that it occupies very little space in the place where it is set.”
Ramelli never ended up building this
device, but the bookwheel has long intrigued those who study the history
of the book—and in 2018, a group of undergraduate engineering students
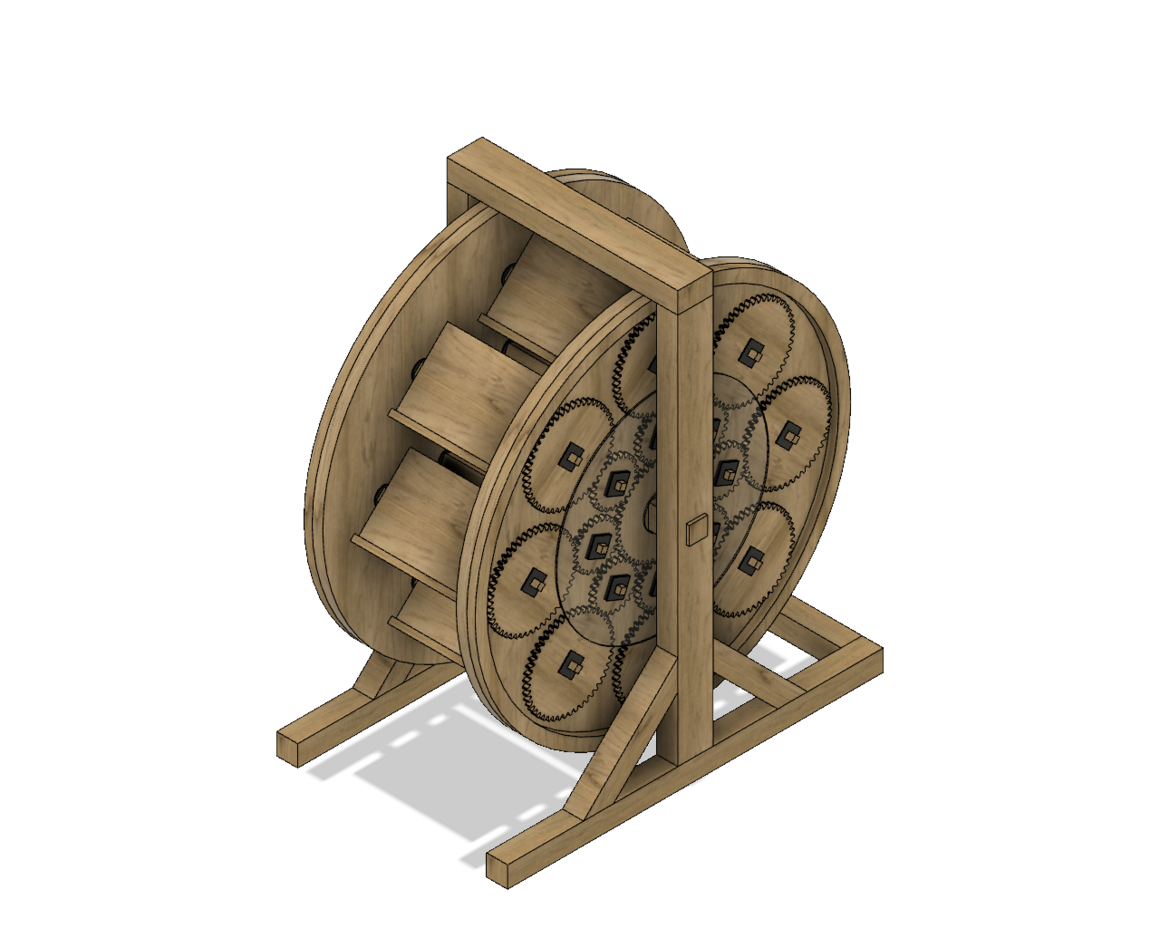
at the Rochester Institute of Technology set out to build two. They
began by diligently studying the Italian engineer’s illustration, then
procured historically accurate materials, such as European beech and
white oak. With the help of modern power tools and processes, such as
computer modeling and CNC routing, they brought it to life. “Cutting the
gears by hand would have taken a considerate amount of time,” says RIT
graduate Ian Kurtz. “The actual construction may not have been worth the
time with 16th-century techniques … I think Agostino was more so
showing his understanding of how gear systems worked.”
Today, one wheel resides at the Melbert B. Cary Jr. Graphic Arts Collection
at RIT’s Wallace Library, and the other at the University of
Rochester’s Rossell Hope Robbins Library. Each weighs about 600 pounds
and has room for eight books; users can take a seat and spin the wooden
cases, which are carefully weighted to avoid unintended movements. It’s
also worth getting close to observe the core mechanism: a complex,
epicyclic gearing system that consists of outer gears rotating around a
central gear, much like planets moving around the sun.
Ramelli’s design likely inspired similar
wheels that were built in the 17th and 18th centuries, several of which
still exist, but it was probably more complicated than it needed to be.
“There are simpler objects you could build that would accomplish mostly
the same goals,” says Matt Nygren, another former student who built the
wheels. “This is more extravagant than it is entirely practical.” A more
efficient bookwheel, he adds, would be one structured like a Ferris
wheel, with hanging, weighted cradles rather than shelves that move
along a gear system.
Simpler bookwheels did precede Ramelli’s
rotating lectern. Readers in the late Medieval Period could sit by a
book carousel, which rotated open books along a horizontal plane, like a
Lazy Susan, and didn’t require side supports. Steven Galbraith, curator
of the Cary Collection, suspects that the Italian engineer was trying
to improve this design and cater to an increasing need to
cross-reference books, which were often large and heavy. “Through the
16th century, books are beginning to talk to each other a lot more—one
might reference another—so a bookwheel could have been convenient,” he
says. “Some scholars say it’s the beginning of the idea of hypertext,
the idea that a reader can sit in one spot and have access to multiple
texts at once.” (That concept is all too familiar today, in the age of
hyperlinks, search engines, and browser tabs.)
The Cary Collection’s
wheel can be used for individual reading research, but it is also often
used as a teaching tool. At RIT, Juilee Decker, an associate professor
of museum studies, has had her classes design visitor experiences around
the bookwheel. Students have created
videos, games, and instructional material about the device, along the
way developing skills related to digital content curation and audience
engagement. Museums have also expressed interest in the wheel: In
Russia, the Museum of Languages of the World built its own version
according to the RIT team’s plans, which are published online. The University of the Pacific in California has also expressed interest in acquiring one.
Bibliophiles, particularly those who can relate to tsundoku—the
Japanese term describing the habit of acquiring books without reading
them—might want to own Ramelli’s bookwheel, too. But while Kurtz and
Nygren acknowledge that the apparatus is historically significant, they
both believe it doesn’t serve much of a practical purpose, from an
engineering perspective. “I dont think it’s something you should buy and
try and keep in your living room—nowadays there are better tools for
the job,” Nygren says. “But it’s certainly an eye-catching thing, and
one of the fanciest ways I can think of for storing books.”
© 2020 Atlas Obscura. All rights reserved.